Sunday, September 13, 2009
ADSL Technology
The basic idea behind the technology is the need to transfer large amounts of information from the exchange to the subscriber's home (downloads of games, movies, etc.) while in the upstream channel (from the subscriber's home to the x exchange) a slower channel is sufficient, enabling communication with the content provider, sending emails or uploading to FTP servers.
ADSL technology uses the existing copper infrastructure deployed all over the country, making the broadband network possible without having to set up a new infrastructure. The technology enables maximum utilization of the typical bandwidth of the copper lines by means of complex data processing and encoding. Instead of using frequencies of 4 kHz, as was done until now, we use a range of frequencies between 0 KHz and 1.1 MHz, where standard ADSL system use 256 frequency channels (for the information moving downstream to from the exchange to the subscriber and for the upstream channel) with a bandwidth of 4 KHz per channel, thus enabling the transfer of much more information.
Technical Characteristics of ADSL
v Asymmetric distribution of the rate – up to 8 Mbps on the downstream channel and up to 768 on the u[stream channel.
v The range of frequencies is higher than the basic telephone frequency and up to a 1 MHz frequency.
v It is enabled on a regular analog telephone line or on an ISDN line.
v All the features of the line are maintained (such as conference call, call waiting, etc.).
v It is possible to surf the Internet and talk on the same line simultaneously (the use of filters does away with the need for a separate line for the Internet).
Access Method Technology
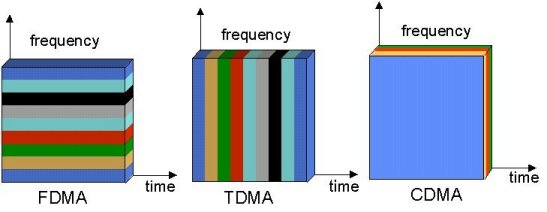
Technology plural access is method used to some information canals transmission at frequency band which have been determined. In general there are three kinds of accessing plural that is FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA.
FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access) Technique FDMA is technique access plural which generally used by cellular communication. Where delivered information signals through transmission media which is same to be differentiated frequency to signal every, that way between information one with other information can transmitted and accepted differentiated of frequency.

Spectrum RF for the technique of FDMA
Spectrum RF for the technique of TDMA
CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) Technique CDMA is technique using code to differentiate between information which is one with other at same transmission channel, this technique not affect by transmission time and frequency, or this technique can some information transmitting with same frequency and during which at same time. So that limitation transmission media limited by bandwidth not make problems by using this technique.

Spectrum RF for the technique of CDMA
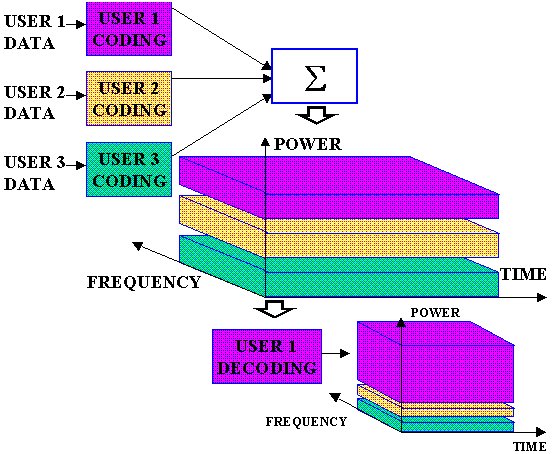
Basic concept of CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) is communications system which use concept of cellular where cell is constrain for allocation used frequency and cell used constrain to determine customer constrain to service don’t customer which don’t service. Even problems the services amount or channels can overcome with system of multiplex just remain to there constrain use technique of multiplex, so that solution or constrain cell focus will not become effective again. Single way able to overcome this problem is improved performance of system multiplex. Temporarily this system of multiplex felt have some excesses by improving service capacities needn't again minimize physical of cell. Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) is method access with user which a lot occupy one same cell areas and use same channel transfer of information (Communications). Usage of same channel have the meaning of every user same frequency and same during to communicated. Because using same frequency and during which at the same time between user, hence to differentiate user which is one with system the other CDMA use technique spread spectrum. Spectrum Spread is transmission technique by using code the method of spreading. That Code spreading is used as identification or can be conceived by address for every user which it uses same frequency and spanning same time also with the other user, so that receiver user will ear. Access plural is method used to some discussion channels frequency bands which have been determined.
Wireless Internet Service
One day customer services of the telecommunication operators received a call from a customer to complaint their data service. A customer said that they have lied to all their customers. Telecommunication operators promised to give us the best speed to their Wireless Internet Access through CDMA platform. But what customers get is not what they have been promising. Customer complaint since the Wireless Internet Access’ speed is very slow. Meanwhile another customer called to complaint with different cases. They have been trying so many times to connect data service of telecommunication operator but always failed. And finally they said that Wireless Internet Access offered by telecommunication operators is suck. It has more disadvantages rather than advantages.
I think whichever telecommunication operators that offer Wireless Internet Access CDMA, GPRS, 3G or EVDO will face the same cases; their will got a lot of complaint their customers. Some of customer’s complaint about the quality of speed, some about network availability and some about tariff that charged to them. Everyday we can see in the news paper regarding to this complaint. They releases a complaint to news paper due to after several complaint they have done to telecommunication operators, there is no improvement. They still face the same problem. Many customers disappointed to Wireless Internet Access offered by several telecommunication
Actually many factors are influence the quality of data service offered by telecommunication operators, CDMA, GPRS, 3G or EVDO. Data service more complicate than voice or SMS services. Many network elements are involved to have data service to their customers. Generally to have voice or SMS service, the network element that involved to these services are;
1. Customers’ handset/mobile phone
2. Base Transceiver Station (BTS)
3. Transmission link
4. Core Network (Mobile Switching Centre (MSC), Home Local Register HLR)
Meanwhile in data services, many others networks are needed in order to this service and as the result new additional network elements will influence the quality of service
In order to have data service (Wireless Internet Access), telecommunication operator must add several networks elements to existing network;
1. Modem to dial up or mobile phone with internet features
2. Internet link to Internet Service Provider (ISP)
3. Connection from telecommunication operators’ office to ISP
4. International connection from ISP to world wide
The problem of Wireless Internet Service could be from any side mentioned above and we need to analyze each complaint deeply to identify from which element the problem coming is and getting the best solution. It is totally different with SMS or voice service once the problems come. The problem could be from customers’ side but since customers did not know a lot about it, they do nothing in their side to resolve the problem. But mostly, the problem of Wireless Internet Service is coming from telecommunication operators’ end. And in some case, it is coming from their ISP partners.
CDMA Overview
For radio systems there are two resources, frequency and time. Division by frequency, so that each pair of communicators is allocated part of the spectrum for all of the time, results in Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA). Division by time, so that each pair of communicators is allocated all (or at least a large part) of the spectrum for part of the time results in Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA). In Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA), every communicator will be allocated the entire spectrum all of the time. CDMA uses codes to identify connections.
 |
| Multiple Access Schemes |
CODING
CDMA uses unique spreading codes to spread the baseband data before transmission. The signal is transmitted in a channel, which is below noise level. The receiver then uses a correlator to despread the wanted signal, which is passed through a narrow bandpass filter. Unwanted signals will not be despread and will not pass through the filter. Codes take the form of a carefully designed one/zero sequence produced at a much higher rate than that of the baseband data. The rate of a spreading code is referred to as chip rate rather than bit rate.
See coding process page for more details.
 |
| CDMA spreading |
CODES
CDMA codes are not required to provide call security, but create a uniqueness to enable call identification. Codes should not correlate to other codes or time shifted version of itself. Spreading codes are noise like pseudo-random codes, channel codes are designed for maximum separation from each other and cell identification codes are balanced not to correlate to other codes of itself.
See codes page for more details.
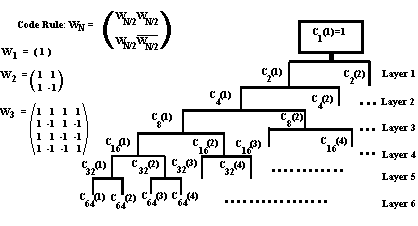 |
| Example OVSF codes, used in channel coding |
THE SPREADING PROCESS
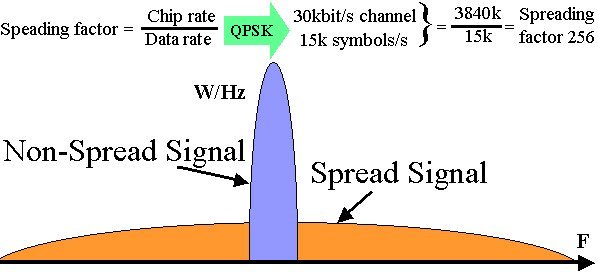
WCDMA uses Direct Sequence spreading, where spreading process is done by directly combining the baseband information to high chip rate binary code. The Spreading Factor is the ratio of the chips (UMTS = 3.84Mchips/s) to baseband information rate. Spreading factors vary from 4 to 512 in FDD UMTS. Spreading process gain can in expressed in dBs (Spreading factor 128 = 21dB gain).
See spreading page for more details.
 |
| CDMA spreading |
POWER CONTROL
CDMA is interference limited multiple access system. Because all users transmit on the same frequency, internal interference generated by the system is the most significant factor in determining system capacity and call quality. The transmit power for each user must be reduced to limit interference, however, the power should be enough to maintain the required Eb/No (signal to noise ratio) for a satisfactory call quality. Maximum capacity is achieved when Eb/No of every user is at the minimum level needed for the acceptable channel performance. As the MS moves around, the RF environment continuously changes due to fast and slow fading, external interference, shadowing , and other factors. The aim of the dynamic power control is to limit transmitted power on both the links while maintaining link quality under all conditions. Additional advantages are longer mobile battery life and longer life span of BTS power amplifiers
See UMTS power control page for more details.
HANDOVER
Handover occurs when a call has to be passed from one cell to another as the user moves between cells. In a traditional "hard" handover, the connection to the current cell is broken, and then the connection to the new cell is made. This is known as a "break-before-make" handover. Since all cells in CDMA use the same frequency, it is possible to make the connection to the new cell before leaving the current cell. This is known as a "make-before-break" or "soft" handover. Soft handovers require less power, which reduces interference and increases capacity. Mobile can be connected to more that two BTS the handover. "Softer" handover is a special case of soft handover where the radio links that are added and removed belong to the same Node B.
See Handover page for more details.
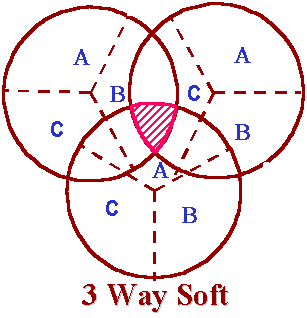 |
| CDMA soft handover |
MULTIPATH AND RAKE RECEIVERS
One of the main advantages of CDMA systems is the capability of using signals that arrive in the receivers with different time delays. This phenomenon is called multipath. FDMA and TDMA, which are narrow band systems, cannot discriminate between the multipath arrivals, and resort to equalization to mitigate the negative effects of multipath. Due to its wide bandwidth and rake receivers, CDMA uses the multipath signals and combines them to make an even stronger signal at the receivers. CDMA subscriber units use rake receivers. This is essentially a set of several receivers. One of the receivers (fingers) constantly searches for different multipaths and feeds the information to the other three fingers. Each finger then demodulates the signal corresponding to a strong multipath. The results are then combined together to make the signal stronger.
Overview UMTS
3G Systems are intended to provide a global mobility with wide range of services including telephony, paging, messaging, Internet and broadband data. International Telecommunication Union (ITU) started the process of defining the standard for third generation systems, referred to as International Mobile Telecommunications 2000 (IMT-2000). In Europe European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) was responsible of UMTS standardisation process. In 1998 Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) was formed to continue the technical specification work. 3GPP has five main UMTS standardisation areas: Radio Access Network, Core Network, Terminals, Services and System Aspects and GERAN.
3GPP Radio Access group is responsible of:
3GPP Core Network group is responsible of: 3GPP Terminal group is responsible of: 3GPP Services and System Aspects group is responsible of: Third Generation Partnership Project 2 (3GPP) was formed for technical development of cdma2000 technology which is a member of IMT-2000 family. In February 1992 World Radio Conference allocated frequencies for UMTS use. Frequencies 1885 - 2025 and 2110 - 2200 MHz were identified for IMT-2000 use. See the UMTS Frequency page for more details. All 3G standards are still under constant development. In 1999 ETSI Standardisation finished for UMTS Phase 1 (Release '99, version 3) and next release is due December 2001. UMTS History page has a list of all major 3G and UMTS milestones. Most of the European countries and some countries round the world have already issued UMTS licenses 2. UMTS Services UMTS offers teleservices (like speech or SMS) and bearer services, which provide the capability for information transfer between access points. It is possible to negotiate and renegotiate the characteristics of a bearer service at session or connection establishment and during ongoing session or connection. Both connection oriented and connectionless services are offered for Point-to-Point and Point-to-Multipoint communication. Bearer services have different QoS parameters for maximum transfer delay, delay variation and bit error rate. Offered data rate targets are: either by beauty contest or auctions. UMTS network services have different QoS classes for four types of traffic: UMTS will also have a Virtual Home Environment (VHE). It is a concept for personal service environment portability across network boundaries and between terminals. Personal service environment means that users are consistently presented with the same personalised features, User Interface customisation and services in whatever network or terminal, wherever the user may be located. UMTS also has improved network security and location based services. 3. UMTS Architecture A UMTS network consist of three interacting domains; Core Network (CN), UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN) and User Equipment (UE). The main function of the core network is to provide switching, routing and transit for user traffic. Core network also contains the databases and network management functions. The basic Core Network architecture for UMTS is based on GSM network with GPRS. All equipment has to be modified for UMTS operation and services. The UTRAN provides the air interface access method for User Equipment. Base Station is referred as Node-B and control equipment for Node-B's is called Radio Network Controller (RNC). UMTS system page has an example, how UMTS network could be build. It is necessary for a network to know the approximate location in order to be able to page user equipment. Here is the list of system areas from largest to smallest. 4. Core Network The Core Network is divided in circuit switched and packet switched domains. Some of the circuit switched elements are Mobile services Switching Centre (MSC), Visitor location register (VLR) and Gateway MSC. Packet switched elements are Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) and Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN). Some network elements, like EIR, HLR, VLR and AUC are shared by both domains. The Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is defined for UMTS core transmission. ATM Adaptation Layer type 2 (AAL2) handles circuit switched connection and packet connection protocol AAL5 is designed for data delivery. The architecture of the Core Network may change when new services and features are introduced. Number Portability DataBase (NPDB) will be used to enable user to change the network while keeping their old phone number. Gateway Location Register (GLR) may be used to optimise the subscriber handling between network boundaries. MSC, VLR and SGSN can merge to become a UMTS MSC. 5. Radio Access Wide band CDMA technology was selected to for UTRAN air interface. UMTS WCDMA is a Direct Sequence CDMA system where user data is multiplied with quasi-random bits derived from WCDMA Spreading codes. In UMTS, in addition to channelisation, Codes are used for synchronisation and scrambling. WCDMA has two basic modes of operation: Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) and Time Division Duplex (TDD). UTRAN interfaces are shown on UMTS Network page. The functions of Node-B are: The functions of RNC are: 6. User Equipment The UMTS standard does not restrict the functionality of the User Equipment in any way. Terminals work as an air interface counter part for Node-B and have many different types of identities. Most of these UMTS identity types are taken directly from GSM specifications. UMTS mobile station can operate in one of three modes of operation: UMTS IC card has same physical characteristics as GSM SIM card. It has several functions: |
Friday, September 4, 2009
Making New Connections Speedy

2. Then click - New Connection Wizard

3. Window appears "New connection wizard", click Next
4. Select "Connect to the internet", click Next
5. Select "Setup my connection manually", click Next
6. Select "Connect using a broadband connection that requires a username and password", click Next
7. Fill ISP Name, Ex: speedy, click Next
8. Fill Username,password, and Confirm Password
Example:
Username: 111802100xxx@telkom.net
Password: xxxxxxxxxx
Confirm Password: xxxxxxxxxx
Click Next
9. Then klik checkbox "Add a shortcut to this connection to my dekstop", click Finish.
by TELKOM Speedy Marketing Division
Tuesday, September 1, 2009
ADSL, Configuration for Telkom Speedy

ADSL modem acts as Bridge
DSL (digital subscribe line asyncronus) as the primary tool to connect a PC to a home phone line (fixed phone / PSTN) to be connected to the Internet is increasingly recognized by many people.
Brands that are available in the market for this ADSL modem, including Prolink, Billion, Linksys, Aztec, and many more. But how to configure the ADSL modem we usually make as a mediator Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) into a bridge.
Congenital Speedy ADSL modem by default, usually by Speedy advertiser your home or office acted as a mediator PPPoE. In fact, the role of an ADSL modem with PPPoE setting is less the maximum. If you want more than just according to the rules, it is necessary to play your ADSL modem is more than just a virtual protocol only.
We can change the ADSL modem which we use as a bridge. Role bridge here is like a 'private bridge' that connects your computer to the routing lengsung beginning of Speedy network. In addition, pengkonfigurasian ADSL modem as a bridge also gives us more advantages in overcoming the problems with dynamic ip is applied to Speedy.
Setting ADSL modem as a bridge, member We can control our internet access directly from a computer that we use without having to deal again with an ADSL modem. In other words, all you need with a direct Internet connection can we operate through operating system that we use. Here we will explain about how to configure your ADSL modem as a bridge.
The following examples use the Aztec brand ADSL modem.
* Open Internet Explorer. Way, click start-all programs-internet explorer
* In the browser URL box, type the address into your ADSL modem. Usually use the address 192.168.1.1 or 10.0.0.1
* Enter your username and password your ADSL modem. Then press the login button.
* Once in the main view mode, click on the setup options
* In the WAN menu, select the connection 0. Typically, the default configuration of an ADSL modem connection is put on setting connection 0.
* After the new display appears on the right, you can simply press the down arrow that is on the box type. Then select the bridge.
* On the bridge option encapsulation settings, select LLC.
* The PVC settings menu, fill in the VPI and VCI according to your region. Check this info on the Undernet. Configuring VPI and VCI for Surabaya and its surroundings, the value of the VPI: VCI = 0: 35
* On the choice of QoS (Quality of Service), select UBR.
* If the process is complete, click the button here apply.Di outlines your ADSL modem is acting as a bridge. You can see the outline of the configuration on the ADSL modem and applying it to the ADSL modem you use (other than the Aztec brand), because this step is a global step that can be applied to all the brands you change modem.Setelah your ADSL modem into a bridge, then the practical Your interner connection is lost.
For more mengoneksikan internet, here are steps you can do:
* Click Start - Settings - Control Panel - Network Connection.
* After that came the display of the Network Connection. Create a new connection by pressing the Create New Connection.
* After that will come a new look. At first view, press the Next button.
* After that, select Connect to the Internet, then press the Next button.
* After that, select the option Set up my connection manually. After that press the Next button.
* Next, select the option Connect using a Broadband connection that requires username and password. After that press the Next button.
* In the Connection Name, fill in the ISP Name box to your liking. Suppose you are content with Speedy_saya name. Then press Next.
* Next insert your username and password. This username and password in accordance with the username and password that you get from Telkom. If you could change your password, you must enter the password. After that, press the Next button.
* End the process by pressing the Finish button.
* After the login display will appear as when you first use telkomnet @ instant. Here, enter your username and password from your Speedy. Then press connect.
* If your username and password correctly, then your internet connection will go well. If not then the connection fails. Make sure you have entered your username and password with benar.Dari here, we have succeeded in changing our ADSL modem into bridge, and control of our Internet access directly from the Operating System that we use.
Good luck ..
Saturday, August 29, 2009
ADSL speedy advantage
Unlike the wireless broadband access where access to the shared customer base stations, ADSL access from the modem individual customers to the nearest DSLAM node, where each customer's own port occupies a fixed (dedicated port).
Connections can be shared
You can menshare your connection at home or at work using a switch or wireless access point (WiFi hotspot).
Free Connection Barriers in the Domestic Backbone
Each node DSLAM directly linked with gigabit connections to the metro ethernet network with a capacity of regional up to 10 Gbps to Bras (broadband remote access server) which is a gateway service Speedy service. Next Bras will direct traffic from the direction Speedy:
- International Gateway
- Internet in the country through peering with OpenIXP, other ISPs, content providers and domestic and foreign large-scale.
- Local broadband content non-internet.
The Convenient Connections to the Gateway International
Telkom provides international gateway capacity is very large to be used simultaneously by Speedy users with certain settings, but still feels good to surf the internet enjoy a variety of content around the world.
Simultaneously Internet Phone Line
ADSL technology enables the distribution of data and voice simultaneously through a regular phone line. During the Internet connection used, phone service, fax, and even dial-up Internet can still be done as usual.
Broadband Content Via Intranet Speedy
Enjoy full access to unlimited broadband full-service local content through an intranet connection Speedy (non-internet). You can access the web content TV, games, a variety of multimedia content, and share files through a special connection that can only be accessed by Speedy.
SPEEDY
Monday, August 24, 2009
About Telkom

PT Telekomunikasi Indonesia, Tbk. (TELKOM) is a provider of information and telecommunication (InfoComm) service providers and the telecommunications network and the complete (full service and network providers), which in Indonesia. TELKOM (hereinafter called the Company or the Company) does not provide services to mobile phone cable (fixed wire line), services, wireless phone does not move (fixed wireless), mobile telephone services (cellular), data & Internet and network & interconnection either directly or through the association of the company.
Until 31 December 2007 the number of customers, TELKOM as 63.0 million subscribers who are customers of the phone cable does not move a number of 8.7 million phone customers do not move some 6.4 million wireless subscribers and 47.9 million mobile phone service subscribers. Growth in the number of TELKOM subscribers in 2007 was 29.9%.
In line with TELKOM's vision to become a leading company in the area of InfoComm regional and realize the TELKOM Goal 3010 various efforts have been made TELKOM to keep winning and leading on all products and services.
Results from these efforts is reflected in market share of products and services that excel in the telecommunications between the players. During the year 2007, TELKOM has received several awards both from within and abroad, among them:
Indonesia's Best for Shareholders' Rights and Equitable Treatment of ASIAMONEY magazine, Top Brand Award 2000-2007 from the Frontier Consulting Group, Zero Accident Award from the Ministry of Manpower and Transmigration, The Best CDMA Provider, Call Center Award 2007, the iMac's Award 2007 Frontier Consulting Group, 2007 Marketing Awards, Anugerah Business Review 2007, Anugerah Juara Umum Nasional Media PR 2007, ICSA 2007, Best Social Reporting Isra 2007, the Fabulous 50, Best IT Project of SAP, Value Creator Award 2007 Award 2007 and the Investor.
TELKOM shares per 31 December 2007 is owned by the Indonesian government (51.82%) and public shareholders (48.18%). TELKOM shares registered in the Indonesian Stock Exchange (Bei), New York (NYSE), London Stock Exchange (LSE) and the Tokyo Stock Exchange, without recorded. TELKOM's share price in the Bei at the end of December 2007 increased 0.5% to Rp 10,150 from Rp 10,100 in the same period in 2006.
Market capitalization value stocks TELKOM at the end of the year 2007 of Rp 204,624 billion or 10.3% of market capitalization Bei
With the achievement and recognition earned TELKOM, control the market for each of its business portfolio, strong financial performance and growth potential in the future, at this time become a model corporate TELKOM Indonesia answer.
Telkom Speedy is an ISP in Indonesia
After May 2008, they increase their bandwidht speed to 1 Mbps (before 384 kbps), and we can feel the speed was increased significantly. Although at the some time the connection was slower than usual.
Telkom Speedy offers some Internet Connection Package :
- Speedy Personal : Bandwidht 1000 MB / month, Rp. 200.000
- Speedy Professional : Bandwidht 3000 MB / month, Rp. 400.000
- Speedy Office : Unlimited, Rp. 750.000
- Speedy Warnet : Unlimited, Rp. 1.750.000
Starts from 1 August 2008, now speedy customers on TELKOM Divisi Regional V (East Java) can enjoy unlimited usage of internet connection from 8 PM to 8 AM
WHAT IS SPEEDY ?

What is Speedy?
SPEEDY is the product of the Internet access service end-to-end from PT. TELKOM, TELKOM with the base technology Asymetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL), which can distribute data and voice simultaneously through a single phone line with the normal speed which are pledged with the service package, which was launched from the modem to Bras (Broadband Remote Access Server).
What is DSL?
ADSL (Asymetric Digital Subscriber Line) technology is a modem that works on the frequency between 34 kHz to 1104 kHz. This is the main cause of the difference in speed transfer of data between the ADSL modem with a conventional modem (which works on the frequency of below 4 kHz). ADSL advantage is the ability to provide high-speed Internet access and voice / fax simultaneously (in the customer using the line Splitter to separate the phone and channel modem).
Are all the phone can be used for Speedy?
Not all the phone network can be used to service Speedy. Contact Customer Care Telkom 147 for more information
What is the understanding and upstream?
1. Downstream is the speed of data flow when customers do with a maximum download speed of up to the ADSL connection Speednya (384 Kbps).
2. Upstream speed the flow of data is when customers do with the maximum upload speed of up to 64 Kbps
What if I forget my password?
Take the contract or subscription charges with evidence last SPEEDY pay to the nearest Plasa telcom. As evidence subscribe to request a new password
What administrative requirements that must be met?
1. Provide a copy of ID / SIM / Passport Speedy customers.
2. Signing of the Contract Subscription Speedy research the materei Rp.6.000, --
3. No charges have arrears of payment and Speedy Phone Faximile or in the installation of the same address, both on behalf of itself and on behalf of the Personal / Company / Agency / Institution, or any name as pengontrak / or tenants and users and the place or live at the address where Speedy registered facilities.
Untuk informasi lebih lanjut hubungi Customer Care Telkom 147 For more information contact Customer Care Telkom 147
What should I prepare?
1. The device computer, a modem provided by the customer
2. Minimum standard technical specifications of the computer (the minimum fun):
a. Pentium II Processor Pentium II Processor
b. Ram 64 MB 64 MB of RAM
3. Hard drives with a capacity of 2 GB if technically required replacement modem to get a new type of service, the responsibility penyediaannya become fully customer.
What are provided by Telkom?
By choosing Speedy as a solution you need access to the Internet then you will get service from Telkom as follows:
1. Spliter installation in customer premises (the customer side of the house)
2. Warranty Speed Internet Access to Broadband RAS
3. Line in accordance with the type of service
4. Internet access through ISP TELKOMNET
How do I choose the ADSL modem?
Tips to get a good ADSL modem is as follows:
1. Whether the modem is used for some PC or only one PC. Jika untuk satu PC cukup modem dengan 1 port USB dan atau 1 port ethernet, If enough for a PC modem with 1 USB port and ethernet port or 1, but when will be used for some of the PC modem can be used with some ethernet port (functioning as a hub). Most types of modems sold in the market when this is a modem router that can save the connection configuration SPEEDY (username and password) in memory modem, so that when the modem is turned on and connected to a phone line, the modem will automatically connect SPEEDY (automatic login) , Even if the computer is connected to the modem is not turned on.
2. Use a modem compatible with the operating system from your PC such as Windows or Linux. From experience in the field, there are several types of USB modems that are not compatible with Windows 98 or Windows 2000.
3. If you have sufficient funds better to use the modem settings that have the ability through the web as can be operated with various types of operating systems and browsers and easy to operate.
Why can not I connect to Speedy?
1. SPEEDY to connect, the ADSL modem connection implement 2, the connection from the ADSL modem to the Digital Multiplekser in STO and the nearest connection to the Bras with the username and password each customer.
2. To see the status of the ADSL connection and connect to the already Up Bras, can be seen in the ADSL connection status monitoring and Internet Connection Status Monitoring in the modem (via the web interface of each type of modem).
3. As a first step, some time switch off the modem and then on again
4. SPEEDY If the connection is still not succeed, interruption of this report to the customer care SPEEDY 147, and the status of connection to that seen in speedu modem unutk accelerate the resolution of interference that occurs.
I have been connected to the Speedy but I can not browising?
1. Sebagai langkah awal, matikan modem dan hidupkan kembali untuk melakukan koneksi baru. As a first step, turn off the modem and turn back to make new connections.
2. If not successful, the detection LAN card with off (disable) and the switch back by clicking the Enable (Control Panel - Network Connection - LAN Connection).
3. Internet browser application should be updated with the latest version.
4. Make sure your PC is not infected with the virus.
I deleted the settings, and how to reset the settings?
1. Make the ADSL modem configuration through a web-based applications provided by the manufacturer. If less clear vendor / store where you buy a modem.
2. See if there are changes to the user & password Speedynya. Jika tidak, lakukan langkah ke-3. If not, do step-3.
3. If your PC is infected the virus, get rid virusnya first.
4. Make connections with Speedy to enter a user & password.
5. Rebooting your PC, make sure that the LAN card has been detected appear with the Network Connection icon in the lower right corner.
Why is my slow Internet?
Speedy connection stability influenced by several things, such as the total traffic on the network, the quality of the phone network, the number of applications / browser active on the computer, health and the PC (free of the virus). When one of these things happen so can cause your slow Internet connection
Usage & Billing
What is the usage, download and upload?
Usage is the number of bytes that is used during the activity Internet access.
Download the activity is access to the Internet to move data / files / applications that are transferred by the machine after Internet users make requests to the data / files / applications on a web page.
Upload is the activity of Internet users when a request to the data / files / applications in a web page.
How to calculate the usage Speedy?
1. When customers sign / light modem (for modem router), billing system will record the user id used, the start time session and the IP Address provided.
2. When customers log out / turn off the modem (for modem router), billing system will record the user id is used, time and number of stops session usage (upload and download).
3. Billing system will send data session this customer (customers after logout) to the data base in telkomspeedy.com to be seen by customers. Proses pengiriman data dilakukan setiap 10 menit. The process of data transfer is done every 10 minutes.
4. After one month, all data usage per customer for diakumulasikan processing charged.
Security
1. Do not let other people know your password
2. Make sure you have the User and Password for the DSL modem setup with the new User and Password, consisting of at least 6 characters
3. Make sure you change the password Speedy with a new password consisting of at least 6 characters and do a combination of further changes periodically.
4. Make sure you have a non-me-port switch-80 DSL modem to the 'WAN' or downloading'Disable 'facilities' Remote Admin' devices at DSL customers
5. Make sure you have an on-going facilities' Firewall 'in the device or DSL modem in Terminal Computer
6. Make sure the mode 'Bridging DSL' you only use when you have a knowledge of computer and networking with the category of 'Advance'
SPEEDY Time Based
Deskripsi Description
Speedy Service Package is where the cost is calculated based on the time of connection to the Internet, not based on the number of packages or data downloaded or uploaded. Methods such as these will subscribe for customers who often have to download the large amount. By choosing the appropriate download time (adjusted with the traffic Speedy other users), then the customer will get the download package with a big price is relatively cheaper.
How to Subscribe
Contact the nearest Plasa Telkom.
Mutation Service
Speedy existing customers (volume based) are allowed to change the package layananannya. Changes in this package will be valid in the month of n + 1. Customers are allowed to change the package of services at any time by observing the provisions above.
Equipment needed
Tools / modem / router that is required with the Service Pack Speedy other. Please note, in the timed base this method, your charges will be calculated based on the durable connections, therefore, turn off the modem / router when you do not use.
taked from PT.TELKOM







